+86-731-89578196
+86-731-89578196
 [email protected]
[email protected]
- Home
- Our Company
-
Products
Sputtering Targets

- Industries
- Blog
- FAQ
- Contact Us
The target bonding methods are recommended for sputtering targets/ Indium bonding vs elastomer bonding
views, Updated: 2021-09-21
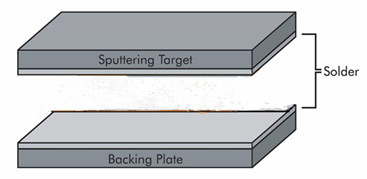
Target bonding is an important process to use solder to bond sputtering targets to a backing plate. The sputtering targets are put into the sputtering source cathode inside the chamber (sputtering deposition system). Working at higher power, the target’s surface generates much heat. The solder layer can draw the heat from the target’s surface into the backing plate. The heat is then transferred through the piece of the backing plate and is removed by the cooling water. The target bonding is essential to prevent cracking, warping, and other damage to sputtering targets in the sputtering process. The bonding process can have an interface thermal integrity between the cooling assembly and the target’s surface. It can increase the longer working life for targets to tolerance most heat.
The most common bonding methods are indium bonding and elastomer bonding. What’s the difference between the two methods?
Indium Bonding
Indium is a preferred method used in target bonding because it has the following features:
1. Indium has a good thermal and conductive conductivity, and it’s the most efficient to draw away much heat from the sputtering targets
2. Indium is more malleable than other bonding solders to reduce the cracking risk caused by the mismatch of targets and backing plate in thermal expansion coefficients.
3. The bond can be taken apart, so the backing plate can be reused to save costs.
The limitation of the indium bond is that indium has a low melting point of 156.6°C. If the working temperature is over 150°C, the bond melt and departs from the targets. Thus, the indium bond is replaced by other bond methods sometimes, although most materials can be indium bonded. Most of the pure metal and ceramic sputtering targets can use the indium bonding method.
Elastomer Bonding
Elastomer bond is an alternative method for indium bond when applied at a higher temperature. This bonding method is recommended in the following situations:
1. When the indium bonds are consistently melted during working.
2. The sputtering targets have a low melting point, low density, fragile, and are sensitive to temperature. The elastomer bonding is performed at a low temperature between 50°C and 100°C, so it is gentle on the targets during the bonding process.
3. The elastomer bond does not absorb any moisture, and it’s suitable to handle the cycle between vacuum and atmosphere.
However, the elastomer bond outgases in a vacuum chamber for most polymer-based materials.
These sputtering targets are required elastomer bonding:
Pure metal sputtering targets: Indium (In) sputtering target, Bismuth (Bi) sputtering target, Lithium (Li) sputtering target, Manganese (Mn) sputtering target, Selenium (Se) sputtering target.
Oxide sputtering targets: Cobalt Oxide (CoO) sputtering target, Tin Oxide (SnO2) sputtering target, Strontium Titanate (SrTiO3), Barium Strontium Titanate (Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3), Lithium Orthophosphate (Li3PO4) sputtering target and Lithium battery materials targets.
Other sputtering targets: Aluminum Nitride ( AlN) sputtering target, Germanium Telluride (GeTe) sputtering target.
The following table summarizes the comparison of indium bonding and elastomer bonding
| Bonding Method | Indium bonding | Elastomer bonding |
| Maximum Operating Temperature (℃) | 150 ℃ | 250 ℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mk) | 83 | 54 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (K-1) | 32.1 x 10-6 | 2.2 x 10-4 |
| Electrical Resistivity (ohm-cm) | 8 x 10-6 | 0.0476 |
| Bond Coverage | >95% | >98% |
| Bond Liner Thickness | 0.010" ± 0.003" | 0.01-0.025’’ |
AEM Deposition offers various sputtering targets and also provides indium & elastomer bonding services. We have Copper, Oxygen-free copper (OFHC), Molybdenum, and Stainless steel backing plates to meet customer’s requirements.
LATEST NEWS