Cobalt Powder




Cobalt Powder Description
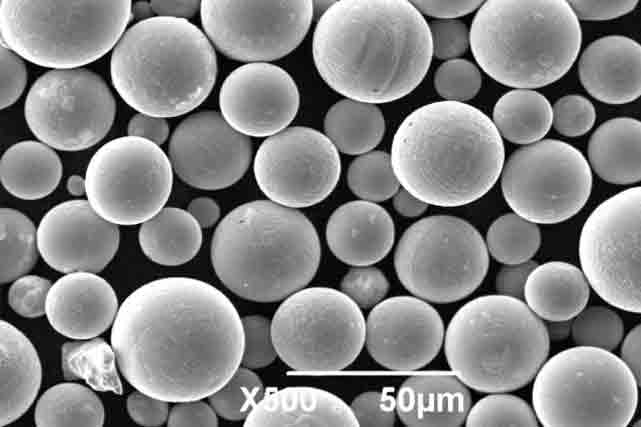
Cobalt powder is a key ingredient in superhard alloy. Its three forms are reduced, electrolytic, and atomized. It determines the bonding property, strength, and toughness of superhard alloy.
Cobalt-based alloy powder is hard alloy powder that resists wear, corrosion, and oxidation at high temperatures. Cobalt is the main ingredient, it also contains chromium and tungsten, and a small amount of nickel, molybdenum, silicon, carbon, niobium and tantalum making up the remainder.
These cobalt alloy powders are used in welding processes that create overlays and also in spray welding processes. These techniques can also be used to create casting and powder metallurgy components, such as high-temperature pressure valves, sawtooth and helical rotor.
Our customers are mostly alloy fabrication and coating companies from all over the world. They ordered a large quantity of cobalt powder from us. AEM is a supplier of high-density powders with customized sizes. If you didn't find the size you need, please email us. If you have any questions about powders, please contact us. We'll be happy to help you out.
Cobalt Metal Powder Application
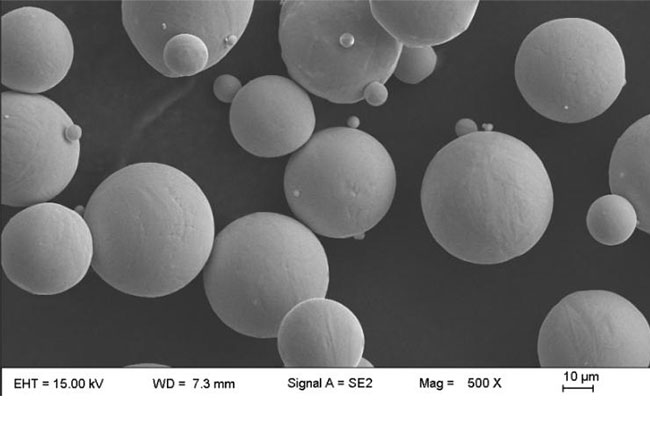
Cobalt metal powder is designed and manufactured for use in high-quality cemented carbide and related products. The hard metal industry demands Cobalt spherical powder that meets high purity, fine particle size, and consistent particle size distribution standards.
Cobalt atomized powder is used to make Diamond Tools. Some of the most common Diamond Tools that are made with Cobalt include Diamond Segments, Tool Wires, Tool Blades, and more. These tools are used for cutting stones like Marble and Granite.
| Grade | Product Name | Chemical Composition (wt%) | Particle Size | Apparent Density (g/cm3) | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-1 | Cobalt powder |
Co: ≥ 99.5% Ni: 0.05 Fe: 0.01 Na: 0.015 Cu: 0.01 Zn: 0.08 Mg:0.008 C: 0.030 S: 0.03 Mn: 0.008 O: 0.50 |
≤ 2 um, -200 mesh, -300 mesh customized sizes avaliable |
0.7 - 1.0 |
Lightgray, electrolytic, Reduced, Atomized |
If you're looking for cobalt powder, we'll work with you to find the best option for your needs.
Spherical Cobalt Based Alloy Powder
Spherical Cobalt Based Alloy Powder is a high-strength, high-temperature resistant alloy powder. It is mainly used in the 3D Printing industry, as well as in other high-temperature and wear-resistant applications. The main components of the alloy are cobalt, nickel, and chromium.
The addition of these elements makes the alloy more resistant to corrosion and wear. In addition, the spherical shape of the powder helps to reduce friction and improve the flow of liquids and gases. As a result, Spherical Cobalt Based Alloy Powder is an essential material for many industries.
Grade: CoCrMo, CoCrMoW, CoCrW
Standard: GB/T 17100, ASTM F75, ASTM F562, GB/T 1480, GB/T 5329, GB/T 8180
Particle Size: 0-20μm, 15-45μm, 15-53μm, 53-105μm, 53-150μm, 105-250μm
Shape: Spherical, Ψ0≥0.85
Appearance: Gray
3D Printing Application: SLM, EBM, LMD
Other Application: PM, MIN, HIP, SP, Welding repair
Package: Vacuum packaging (Aluminum foil bag) or argon-filled protective packaging (Aluminum bottle)
Chemical Composition of Cobalt-based Alloy Powder
|
Chemical Composition (wt%) |
Grade | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoCrMo | CoCrMoW | GH5188 | GH5605 | GH5941 | ||
| Cr | 26-30 | 23.7-25.7 | 20-24 | 19-21 | 19-23 | |
| Mo | 5-7 | 4.6-5.6 | ||||
| Si | ≤1 | 0.8-1.2 | ||||
| Mn | ≤1 | |||||
| Fe | ≤0.75 | ≤0.5 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤1.5 | |
| Ni | ≤0.5 | 20-24 | 9-11 | 19-23 | ||
| Co | Bal. | Bal. | Bal. | Bal. | Bal. | |
| W | ≤0.5 | 4.9-5.9 | 13-16 | 14-16 | 17-19 | |
| C | ≤0.16 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.05-0.15 | ≤0.1 | ||
| Al | ≤0.1 | |||||
| Ti | ≤0.1 | |||||
| P | ≤0.02 | |||||
| S | ≤0.01 | |||||
| B | ≤0.01 | |||||
| O | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | |
| N | 0.13-0.25 | 0.13-0.25 | 0.13-0.25 | |||
| Ta | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 | |||
If you're looking for Spherical Cobalt-based alloy powder, we'll work with you to find the best solution for your needs.
Cobalt Based Alloy Powder (Thermal Sparaying and Welding Powder)
Cobalt-based alloys usually have tungsten and carbon in them. The carbon makes the alloy harder. This happens because the carbon doesn't dissolve in the cobalt very well.
All of these hard parts make the alloy stronger at temperatures that are less than 800 degrees Celsius. The Cobalt-Chromium-Tungsten-Carbide alloys usually have excellent properties like being resistant to high temperatures, oxidation, and thermal fatigue.
When the temperature of Cobalt is below 417 degrees Celsius, it has a hexagonal-closed-packed (HCP) crystal structure which makes it wear resistant. However, when the temperature rises above 417 degrees Celsius, Cobalt transforms from HCP to FCC (face-centered-cubic) crystal structure.This can cause thermal stress and can lead to cracking in the coating or overlay if not preheated to 500-600 degrees Celsius.
If you're looking for Cobalt-based alloy powder, we'll work with you to find the best solution for your needs.
Co-Cr-W
| Grade | Hardness HRC | Chemical Composition | Particle (mesh) | Application | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Si | W | Fe | Mo | Ni | Co | Mn | P | |||||||||||||
| Co01 | 48-54 | 2.4 | 30 | 1 | 12 | ≦3.00 | ≦1.00 | ≦3.00 | Bal. | ≦1.00 | 100/270 | Valve seats, bearing, cutting blades | ||||||||||
| Co03 | 48-54 | 2.3 | 30 | 1 | 12 | ≦3.00 | / | ≦3.00 | Bal. | / | 100/270 | Needle valve seats, guide roils valve seats | ||||||||||
| Co06 | 38-44 | 1.2 | 30 | 1 | 4.5 | ≦3.00 | ≦3.00 | Bal. | ≦1.00 | 100/270、300/500 | Engine values, high temperature pressure valves, turbo engine blades | |||||||||||
| Co156 | 40-45 | 1.6 | 28 | 1.1 | 4 | Bal. | 100/270 | Automotive partis, miliary application | ||||||||||||||
| Co06H | 43-48 | 1.3 | 30 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 3.00Max | 0.8 | 3.00Max | Bal. | 1.0Max | 100/270 | Engine values, high temperature pressure valves, turbo engine blades | ||||||||||
| Co12 | 42-48 | 1.4 | 29 | 1.4 | 8.5 | ≦3.00 | ≦1.00 | ≦3.00 | Bal. | ≦1.00 | 100/270 | High temperature pressure valves, turbo engine blades | ||||||||||
| Co12B | 45-49 | 1.3 | 30 | 1 | 5.5 | 3.0Max | 5 | 10.5 | Bal. | 1.0Max | 100/270 | Saw, guide plates | ||||||||||
| Co12H | 48-53 | 1.7 | 30 | 1.7 | 7 | 2.0Max | 2 | 3.0Max | Bal. | 0.5Max | 100/270 | High temperature pressure valves, saw teeth, extrusion screws | ||||||||||
| Co6113 | 43-48 | 1.8 | 27 | 4 | 6 | Bal. | 100/270 | Resistance to corrosionand wear | ||||||||||||||
| Co107 | 40-44(46-50) | 2 | 35 | 1 | 5 | 2.0Max | 24 | Bal. | 1 | 100/270 | Work herdening | |||||||||||
| Co19 | 48-56 | 1.8 | 31 | 1 | 11 | 3.0Max | 3.0Max | Bal. | 1 | 100/270 | Cutting knives | |||||||||||
| CoF | 37-44 | 1.6 | 26 | 1.1 | 12 | 3.0max | 0.5Max | 22.5 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 100/270 | Engine values | ||||||||||
| CoFH | 38-44 | 1.4 | 28 | 1.2 | 12 | 3.0Max | 0.8 | 22.5 | Bal. | 0.5 | 100/270 | Engine values | ||||||||||
| Co20 | 47-53 | 2.5 | 32 | 1 | 18 | ≦3.00 | ≦1.00 | ≦3.00 | Bal. | ≦1.00 | 300/500 | Bearing sleeves, wear plates | ||||||||||
| Co07 | 30-36 | 0.4 | 26 | 0.9 | 5.5 | 3.0Max | 3.0Max | Bal. | 0.3 | 100/270 | Steam turbine blades, brass casting molds, extrusion molds | |||||||||||
| CoX-40 | 30-35 | 0.8 | 25.5 | 0.4 | 7.5 | 1.0Max | 1.0Max | 10.5 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 0.04Max | 100/270 | Steam turbine pans for resisting high temperature degradation and erosion | |||||||||
| Co31 | 30-35 | 0.4 | 25.5 | 0.8 | 7.5 | 2.0Max | 0.5Max | 10.5 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 100/270 | Steam turbine pans for resisting high temperature degradation and erosion | ||||||||||
| Co694 | 47-53 | 1 | 28 | 1 | 19 | 2.5Max | Bal. | 1 | 100/270 | Steam turbine parts for resisting temperature degradation and erosion | ||||||||||||
| Co25 | 20Max | 0.05Max | 20 | 0.8 | 15 | 3.0Max | 8 | 10 | Bal. | 1.3 | 100/270 | Hot extrusion molds | ||||||||||
| Co306 | 34-40 | 0.4 | 25 | 1 | 2.5 | 4.0Max | 6 | Bal. | 1 | 100/270 | Steel hot rolling shears, clangs, guide rolls | |||||||||||
| Co238 | 20-26 | 0.1 | 26 | 1 | 20 | 3 | Bal. | 1 | 100/270 | Forging dies | ||||||||||||
| Co190 | 57-63 | 3.3 | 26 | 0.8 | 14 | 3.0Max | 1.0Max | 3.0Max | Bal. | 1.0Max | 100/270 | Oil drilling heads | ||||||||||
| Co400 | 48-54 | 0.08Max | 8.5 | 2.5 | 2.0Max | 29 | 1.0Max | Bal. | 0.5Max | 100/270、300/500 | Galvanizing line bearing sleeves and shaft sleeves | |||||||||||
| Co400M1 | 50-54 | 0.08Max | 14 | 2.6 | 0.5Max | 26 | 0.5 | Bal. | 0.1Max | 100/270、300/500 | Resist high temperature orrosion, galvanizing bearing sleeves, shaft sleeves | |||||||||||
| Co400M2 | 46-52 | 0.08Max | 17 | 1.2 | 0.5Max | 22 | 0.5Max | Bal. | 0.5Max | 100/270、300/500 | Resist high temperature corrosion, galvanizing bearing sleeves, shaft sleeves, natural gas engine valves | |||||||||||
| Co800 | 52-58 | 0.08Max | 17.5 | 3.5 | 2.0Max | 29 | 1.0Max | Bal. | 0.5Max | 300/500 | Resist high temperature degradation | |||||||||||
Co-Cr-Mo
| Grade | Hardness (HRC) | Chemical Composition | Particle (mesh) | Application | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Si | Fe | Mo | Ni | Co | Mn | |||||||||||
| Co706 | 38-43 | 1.2 | 29 | 0.5 | 3.0Max | 5 | 3.0Max | Bal. | 1 | 100/270、300/500 | Pressure valves with high temperature corrosion resistance | |||||||
| Co712 | 45-50 | 1.8 | 29 | 0.5 | 3.0Max | 9 | 3.0Max | Bal. | 0.5 | 100/270 | Pressure valves with high temperature corrosion resistance, ectrusion screws | |||||||
| Co701 | 50-56 | 2.5 | 31 | 0.5 | 3.0Max | 13 | 3.0Max | Bal. | 0.5 | 100/270 | Pressure valves with high temperature corrosion resistance, ectrusion screws | |||||||
| Co720 | 54-60 | 2.5 | 33 | 0.5 | 3.0Max | 18 | 3.0Max | Bal. | 0.8 | 300/500 | Pressure valves with high temperature corrosion resistance | |||||||
| Co721 | 18-24 | 0.05Max | 30 | 0.6 | 8 | 4 | 0.3Max | Bal. | 0.7 | 100/270 | Steam turbine erosion-resistant parts | |||||||
Self-fusing Cobalt Base Alloy Powder
| Grade | Hardness (HRC) | Chemical Composition | Particle (mesh) | Application | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Si | W | Fe | Mo | Ni | Co | Mn | B | |||||||
| Co157 | 51-57 | 0.3 | 22 | 1.5 | 5 | 3.0Max | 3.0Max | Bal. | 2.4 | 150/300 | High temperature pressure valves | |||||
| Co158 | 40-46 | 0.8 | 29 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 3.0Max | ≦1.00 | ≦3.00 | Bal. | ≦1.00 | 0.8 | 150/300 | High temperature pressure valves | |||
| Co158V | 45-50 | 1 | 30 | 1.2 | 8 | 3.0Max | 3 | Bal. | 0.3Max | 0.8 | 200/400 | Motorcycle engine valves | ||||
| CoWC35 | 57-63 | 2.4 | 12 | 2.6 | 33 | 3.0Max | 9 | Bal. | 1.9 | 150/300 | Motorcycle engine valves | |||||
| CoSF6 | 40-46 | 0.6 | 18 | 2.3 | 7.5 | 3.0Max | 1.0Max | 14 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 1.7 | 150/300 | Galvanizing line bearing and shaft sleeves | |||
| CoSF12 | 46-52 | 0.9 | 18 | 2.8 | 9 | 3.0Max | 14 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 1.8 | 150/300 | High temperature pressure valves and seats | ||||
| CoSF1 | 52-58 | 1.2 | 19 | 2.8 | 12 | 3.0Max | 12 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 2.4 | 150/300 | High temperature pressure valves and seats | ||||
| CoSF20 | 59-64 | 1.5 | 19 | 3 | 15 | 2.0Max | 13 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 3 | 150/300 | High temperature pressure valves and seats | ||||
| CoSFT400 | 55-60 | 0.1 | 10 | 2.5 | 1.0Max | 22 | 5 | Bal. | 0.5Max | 1.8 | 100/270 | Galvanizing line bearing shaft sleeves | ||||
Spherical Cobalt Based Alloy Powder
| Tantalum Powder | |||
| More Powder |
Related Products of Cobalt Powder
|
Ceramic Sputtering Targets |
||
|
Evaporation Materials Cobalt Pellet Evaporation Material |
Crucibles N/A |
Metal Powders |
 Click to download datasheet about Cobalt Powder
Click to download datasheet about Cobalt Powder
 Unable to find the required data sheet? Click here to send an email and get it.
Unable to find the required data sheet? Click here to send an email and get it.
 Click here to get answers to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ).
Click here to get answers to Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ).